Data Warehousing And Data Mining Lecture Notes Pdf

D ATA W AREHOUSING AND D ATA M INING A Comprehensive guide for students and IT Professionals (Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) Pattern) – New Syllabus ( For B. Sc Computer Science, B.Sc., Software Computer Science, B.Sc.
Machine Learning and Data Mining Lecture Notes. Graham Taylor and James Martens assisted with preparation of these notes. Machine learning provides a. Lecture 03: Data Warehousing and OLAP Technology. Lecture 04: Data Cube Computation and Data Generalization. Lecture 05: Mining Frequent.
Software System, B.Sc. Software Engineering, BCA, M.Sc. Computer Science, M.Sc. Information Technology, M.Sc.
Information System and Management, M.Sc. Software Engineering, MCA, B.E.CSE, B.Tech IT, M.E CSE, M.Tech IT, M.Phil., and IT Professionals.) By Dr.P.Rizwan Ahmed, MCA,, M.Sc.,M.A.,M.Phil.,Ph.D, Head of the Department Department of Computer Applications and PG Department of Information Technology Mazharul Uloom College, Ambur - 635 802, Vellore Dist.
CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgement PART- I DATA MINING Chapter – 1 Introduction 1.1 An Expanding universe of data 1.2 Information and production factor 1.3 KDD and data mining 1.4 Data Mining vs query tools 1.5 Data Mining in Marketing 1.6 Practical applications of data mining 1.7 Learning 1.8 Self-learning computer systems 1.9 Machine learning 1.9.1 Why machine learning is done? 1.10 Machine learning and the methodology of science 1.10.1 Differences between Data Mining and Machine Learning 1.11 Concept Learning Summary Review Question Chapter – 2 Data Mining and the Data Warehouse 2.1 Data Warehouse: Definitions 2.2 Why do we need Data Warehouse? 2. Noting And Drafting Book Free. 3 Designing decision support systems 2.3.1Hardware and software products of a decision support system 2.4 Integration with data mining 2.5 Client/server and data warehousing 2.6 Multi-processing machines 2.7 Cost justification Summary Review Questions.
6.2 Information content of a message 6.3 Noise and redundancy 6.4 Significance of noise 6.5 Fuzzy databases 6.6 The traditional theory of the relational database 6.7 From relations to tables 6.7.1 From keys to statistical dependencies 6.8 Denormalization 6.9 Data mining primitives Summary Review Questions Chapter – 7 Data Mining 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Data 7.3 Information 7.4 Knowledge 7.5 Historical Note: Many names of Data Mining 7.6 Data Mining 7.6.1 Some of the definitions of Data Mining 7.7 Why Data Mining 7.8 Why Data Mining is Important? 7.9 Uses of Data Mining 7.10 Data Mining Models 7.10.1 Verification Model 7.10.2 Discovery Model 7.11 Development of data mining 7.12 Applications of Data Mining 7.12.1 Healthcare 7.12.2 Finance 7.12.3 Retail Industry 7.12.4 Telecommunication 7.12.5 Text Mining and Web Mining 7.12.6 Higher Education 7.13 Basic Data Mining Tasks / Taxonomy of data mining tasks 7.13.1 Prediction methods 7.13.2 Descriptive methods 7.14 Data Mining Vs Database 7.15 Data Mining Vs KDD. 9.4 Data Mining Task Primitives 9.5 Why Data Mining Primitives and Languages?
11.6 Genetic Algorithms Summary Review Question Chapter 12 Data Preprocessing 12.1 1ntroduction 12.2 Why preprocess the data / Need for preprocessing 12.3 Data Preprocessing Techniques / Major Tasks in Data Preprocessing 12.4 Data Cleaning 12.4.1 Missing Data / Values 12.4.1.1 Methods of handling missing data 12.4.2 Noisy Data 12.4.2.1 How to Handle Noisy Data? 18.5.3 K-means clustering 18.5.4 Nearest neighbor algorithm 18.5.5 PAM Algorithm 18.5.5.1CLARA 18.5.5.2 CLARANS 18.5.6 Clustering with genetic algorithms 18.5.7 Clustering With Neural Networks 18.5.7.1 Self-Organizing Feature Maps 18.6 Clustering Large Databases 18.6.1 BIRCH 18.6.2 DBSCAN 18.6.3 CURE Algorithm 18.7 Comparison of Clustering Algorithm Summary Review Questions Chapter 19 Cluster Analysis 19.1 What is Cluster Analysis? 19.2 General Applications of Clustering 19.3 Examples of Clustering Applications 19.4 What is Good Clustering? 19.5 Requirements of Clustering in Data Mining 19.6 Types of Data in Cluster Analysis 19.6.1 Interval-valued variables 19.6.2 Binary Variables 19.6.3 Nominal, Ordinal, and Ratio-Scaled Variables. 19.7 A Categorization of Major Clustering Methods 19.7.1 Major Clustering Approaches 19.8 Partitioning Methods: Basic Concept 19.8.1 K-Means Clustering Method 19.8.2K-Medoids Clustering Method 19.8.2.1 Comparison between K-means and K-medoids 19.8.3 PAM 19.8.4 CLARA 19.9 Hierarchical Methods 19.9.1 Types of Hierarchical Clustering Methods 19.9.1.1 Agglomerative Hierarchical Clustering 19.9.1.2 Divisive Hierarchical Clustering 19.9.2 BIRCH.
22.3 Need for Data Warehousing 22.4 Why Separate Data Warehouse? Summary Review Questions Chapter 32 Operating the data warehouse 32.1 Introduction 32.2 Day-To Day Operations of the Data Warehouse 32.3 Overnight Processing Summary Review Questions Chapter 33 Capacity Planning 33.1 Process 33.2 Estimating the Load 33.2.1 Initial Configuration 33.2.2 How much CPU bandwidth 33.2.3 How Much Memory 33.2.4 How much disk? Summary Review Questions Chapter 34 Tuning and testing the data warehouse 34.1 Tuning the Data Load 34.2 Prioritized Tuning Steps 34.3 Tuning Queries 34.3.1 Fixed queries 34.3.2 AD HOC queries 34. 4 Testing the Data Warehouse 34.4. 1 Introduction 34.4.2 The Testing Terminologies 34.4.3 Testing the operational environment 34.4.5 Testing the database 34.4.5.1 Testing database manager and monitoring tools 34.4.5.2 Testing database features 34.4.5.3 Testing database performance 34.5 Testing the Application Summary.
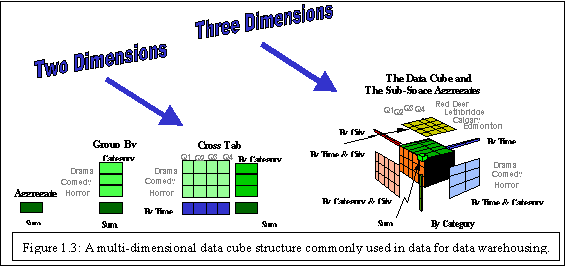
Latest Material Links Link – Link – Link – Link – Link – Link – Link – Link – Link – Old Material Links Link – Link – Link – Link – Link – Please find the more DWDM Notes ppt files download links below UNIT – I Introduction: Fundamentals of data mining, Data Mining Functionalities, Classification of Data Mining systems, Major issues in Data Mining. Data Preprocessing: Needs Preprocessing the Data, Data Cleaning, Data Integration and Transformation, Data Reduction, Discretization and Concept Hierarchy Generation. UNIT – II Data Warehouse and OLAP Technology for Data Mining Data Warehouse, Multidimensional Data Model, Data Warehouse Architecture, Data Warehouse Implementation, Further Development of Data Cube Technology, From Data Warehousing to Data Mining. Data cube computation and Data Generalization: Efficient methods for Data cube computation, Further Development of Data Cube and OLAP Technology, Attribute Oriented Induction.
UNIT – III Mining Frequent Patterns, Associations And Correlations, Basic Concepts. Efficient And Scalable Frequent Itemset Mining Methods Mining Various Kinds Of Association Rules, From Associative Mining To Correlation Analysis, Constraint Based Association Mining.
UNIT – IV Classification and Prediction: Issues Regarding Classification and Prediction, Classification by Decision Tree Induction, Bayesian Classification, Classification by Backpropagation, Support Vector Machines, Associative Classification, Lazy Learners, Other Classification Methods, Prediction, Accuracy and Error Measures, Evaluating the accuracy of Classifier or a predictor, Ensemble methods. UNIT – V Cluster Analysis Introduction: Types of Data in Cluster Analysis, A Categorization of Major Clustering Methods, Partitioning Methods, Density-Based Methods, Grid-Based Methods, Model-Based Clustering Methods, Outlier Analysis. UNIT – VI Mining Streams, Time Series and Sequence Data: Mining Data Streams Mining Time Series Data, Mining Sequence Patterns in Transactional Databases, Mining Sequence Patterns in biological Data, Graph Mining, Social Network Analysis and Multi Relational Data Mining UNIT – VII Mining Object, Spatial, Multimedia, Text and Web Data: Multidimensional Analysis and Descriptive mining of Complex Data objects, Spatial Data Mining, Multimedia Data Mining, Text Mining, Mining of the World WideWeb. UNIT – VIII Applications and Trends In Data Mining: Data mining applications, Data Mining Products and Research Prototypes, Additional Themes on Data Mining and Social Impacts Of Data Mining.
TEXT BOOKS: • Data Mining – Concepts and Techniques – JIAWEI HAN & MICHELINE KAMBER Harcourt India.2nd ed 2006 • introduction to data mining- pang-ning tan, micheal steinbach and vipin kumar, pearson education. REFERENCES: • Data Mining Introductory and advanced topics –MARGARET H DUNHAM, PEARSON EDUCATION • Data Mining Techniques – ARUN K PUJARI, University Press.
Power Iso Crack Torrent Download. • Data Warehousing in the Real World – SAM ANAHORY & DENNIS MURRAY. Pearson Edn Asia.
• Data Warehousing Fundamentals – PAULRAJ PONNAIAH WILEY STUDENT EDITION. • The Data Warehouse Life cycle Tool kit – RALPH KIMBALL WILEY STUDENT EDITION. Note:- These notes are according to the r09 Syllabus book of.In R13,8-units of R09 syllabus are combined into 5-units in r13 syllabus.